Objective of the chapter: Climate of India (Class 5)
You will learn about:
- weather and climate
- difference between weather and climate
- factors that determine climate
- seasons in India
- climatic regions of India
- three heat zones of the Earth
Weather and Climate
Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time. For example, hot, cold or windy. The weather of a place can change quickly within a few days or even from hour to hour.
Today the weather might be rainy in your city but tomorrow it might be a bright and sunny day.
Climate is the average weather condition of a place over a long period of time. Unlike the weather, the climate of a place remains the same for many years.
The climate in the Himalayan Ranges is cold and it remains the same during most months of the year.
The climae in and around Chennai is warm and humid, whereas it is hot and dry in the Thar Desert.
Factors Affecting Climate
Different places in the world have different types of climate. The climate of a place affects the people living there in many ways.
The clothes they wear, the food they eat and the types of houses they live in are all affected by the climate.
The factors that determine the climate of a place are:
- distance from the Equator
- height above the sea level
- distance from the sea
- winds
- the amount of moisture in the air
1. Latitude (Distance From The Equator)
The earth gets heated by the rays of the Sun falling on it. The rays are direct or vertical at the Equator and slanting at the poles.
The slanting rays have to heat up a larger area of the Earth's surface than the direct rays that fall on the equator.
Hence, places near the Equator get heated more than places near the poles.
Also, the Sun's rays have to travel a greater distance through the air at the poles than at the Equator, losing in the process a lot of its heat to the clouds, water vapour and dust present in the air.
Different parts of the Earth, therefore, receive different amounts of heat from the Sun.
Depending on the amount of heat received, there are three climatic or heat zones on the Earth - the Torrid Zone, the Temperate Zone and the Frigid Zone.
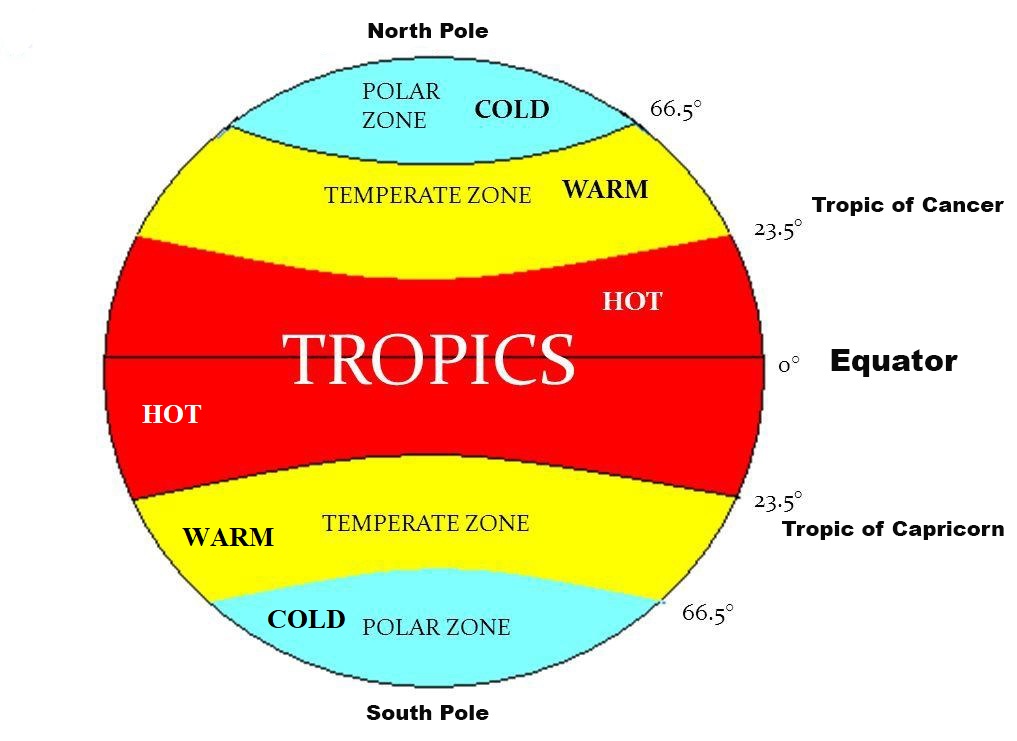
Click here to read about these zones.
2. Height Above Sea Level
Hills are cooler than the plains, even if the two places are the same distance away from the Equator.
The higher you go, the cooler it becomes. The peaks of high mountains are covered with snow throughout the year.
Thus, the higher a place is from the sea level, the cooler is its climate.
3. Distance From The Sea
Water heats up and cools more slowly than land. This affects the climate of places near the sea. They are warmer in winter and cooler in summer than places far away from the sea.
For example, Mumbai is closer to the Equator than Delhi. So, you may think that Mumbai is warmer than Delhi during summer.
But this is not so as Mumbai is situated on the sea coast that makes its climate moderate, neither too hot nor too cold.
4. Winds
Winds flow in particular directions in different parts of the world.
They may be hot, cool, dry, or full of moisture, depending on where they come from.
For example, the monsoon winds from the Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea bring rain to large parts of India.
On the other hand, the hot winds from the Thar Desert make Delhi very hot during summer.
Thus, climate of an area is affected by the winds.
5. Humidity (Amount Of Moisture In The Air)
Humidity is the amount of water vapour in the air. It affects the climate of a place.
The air over the Equator is laden with water vapour, as the heat of the Sun here causes rapid evaporation of the ocean waters. This causes heavy rain in the area. So, the climate near the Equator is hot and wet.
Deserts are formed in places where there is very little humidity, and so it gets very little rain throughout the year.
Seasons in India
India is a very large country with different types of geographic regions. Thus, in India we experience main seasons like summer, monsoon, winter, autumn and spring. The span of these seasons varies from 2.5 to 3 months.
Spring: This season comes just before summer season. It is a pleasant season - neither too hot nor too cold. During this season trees gets new leaves.
Summer: This season begins in March and continue till June in northern part of India. The plains, the desert areas and the plateau regions are very hot during summer season. In early June, most parts of North and Central India sees very high temperatures as a result of “heat waves”. Whereas the coastal areas experience less hot and the hilly areas have pleasant summer. In summer season days are longer than nights.
Monsoon: This season begins in mid-June and continue till August. It is also called the south-west monsoon as the winds blow from this direction.
How monsoon happens? Monsoon wind gets warmed by the heat of the sun. When it blows over the sea the air picks up a lot of water vapour. This rises upwards in the atmosphere where it cool down and becomes water which falls as rain.
Why all places do not get same amount of rainfall? As the monsoon winds travel from one place to another it losses moisture. So the places that receives the early monsoon get more rain as compared to the places where the monsoon reaches later.
Autumn: This season comes before winter. It starts from the end of the monsoon i.e. September and continue till mid-November. It is a beautiful season. During this season trees in some areas shed their leaves.
Winter: This season begins in later part of November and continue till February. The hilly areas and desert areas remain very cold in winter. In winter, the hilly areas experience snow fall also along with rain. The inland areas that are far away from the sea also remain very cold. Coastal areas are less cold. During the winter season the temperature varies from 10 to 15 degree Celsius. In winter season nights are longer than days.
Also Read: Constitution of India for Class 5
Climatic Regions of India
The climate of India very varied, so it is divided into five different climatic regions. These climatic regions are explained below:
- Tropical wet and dry climate: It has hot summer. Some places experiences very heavy rain fall. It has dry winter.The south-eastern coastal areas of India has a winter monsoon.
- Humid subtropical climate: It also has hot summer. This climate experience heavy monsoon rain in the eastern part of India in comparison to the western part. It has cool winter and the northern and hilly areas of India remain cooler. It covers areas such as Delhi, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and some parts of Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal.
- Mountain climate: It is cooler in summer. It gets rain in the monsoon and remain very cold in winter. It covers the Himalayan region of India.
- Semi-arid climate: It has hot summer. It gets more rain than the desert region. It has cold winter. It covers areas of Punjab, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Maharashtra.
- Desert climate: It remains very hot in summer and very cold in winter. It gets little or no rain in the monsoon. It covers some desert areas of Rajasthan.
A. Fill in the blanks.
- The condition of the atmosphere at a particular place and time is called ___________.
- The rays of the Sun fall vertically on land near the ________, but are slanting near the ________.
- The heat zone within which the Equator lies is the ________ zone.
- The heat zone farthest from the Equator is the ________ zone.
- The heat zone which enjoys a mild climate is the ________ zone.
- The amount of water vapour in the air is known as ________.
- As we go up on a mountain, it becomes ________ (cooler/warmer).
- weather
- Equator, poles
- Torrid
- Frigid
- Temperate
- Humidity
- cooler
Also Read: Heat Zones of the Earth (Class 5)
B. True or False.
- Climate changes from day to day.
- The air in deserts has low humidity.
- During the summer months, days are longer near the Equator than far away from it.
- Most places in the Temperate Zone have a mild climate.
- The climate near the Equator is hot and wet.
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
C. Multiple Choice Questions.
- The Climate of a place is affected by
(a) distance from the Equator
(b) humidity
(c) height above the sea level
(d) all of these - Which of these zones receive the maximum heat from the Sun?
(a) Tropical zone
(b) Frigid zone
(c) Temperate zone
(d) All of these receive equal amounts of heat - A city is expected to have a moderate climate if it is
(a) near the Equator
(b) near the sea
(c) near the mountains
(d) near the Poles - If the latitude of a place is 30° N, it lies in the
(a) Tropical zone
(b) North Temperate zone
(c) Frigid zone
(d) South Temperate zone - A city lies on the Equator. It is located on the plains, far away from the coast. Its climate is expected to be
(a) hot throughout the year
(b) cold throughout the year
(c) hot in summers and cold in winters
(d) neither very hot nor very cold
- (d)
- (a)
- (b)
- (b)
- (c)
If you like this chapter - Climate of India for Class 5, please share this post among your friends on Facebook.
Some more important topics of CLASS 5